Basic Terms of Motion
Distance and Displacement
Let S be the length of
the curved path between two points A and B on it as shown in figure. Then S is the distance between points A and B.
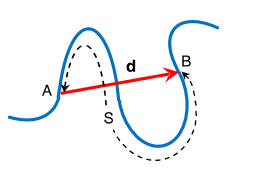 Length of a path between two points is called the
distance between those points.
Length of a path between two points is called the
distance between those points.
Consider a body that moves from point A to point B
along the curved path. Join points A and B by a straight line. The
straight line AB gives the distance which is the shortest
between A and B. This shortest distance has magnitude d and
direction from point A to B.
shortest distance between two points which has magnitude and direction is called displacement.
Displacement is a vector quantity and its unit is meter (m).
Speed and Velocity
Distance covered by an object in unit time is called speed.It tells how much distance is covered in unit time.Its is scalar quantity.
$$ Speed\;=\frac{distance \;covered}{time \;taken}$$
$$ Distance\;= speed \times time$$
$$S = vt$$
Here S is the distance covered and v is speed.
SI unit of speed is meter per second ms-1
The velocity tells us not only the speed of a body
but also the direction along which the body is moving.
Velocity of a body is a vector quantity.
It is equal to the
displacement of a body in unit time.
Rate of displacement of body is called velocity.
$$ velocity\;=\frac{displacement}{time\; taken}$$
$$ displacement\;= velocity \times time$$
$$d = vt$$
Here d is the displacement and v is velocity.
SI unit of velocity is meter per second ms-1
Acceleration
In many cases the velocity of a body changes due to a change either in its magnitude or direction or both. The change in the velocity of a body causes acceleration in it
Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity of a body.
$$ Acceleration = \frac{Change \; in \; Velocity} {time \; taken} $$ $$ Acceleration = \frac{final \; velocity - initial \; velocity}{time \; taken}$$ $$a=\frac{v_{f}-v_{i}}{t}$$Here a is accelearation, vf is final velocity, vi is initial velocity and t is time.
SI unit of accelearation is m/s2
Acceleration of a body is positive if its velocity
increases with time.
The direction of this acceleration is the
same in which the body is moving without change in its
direction.
Acceleration of a body is negative if velocity of the
body decreases.
The direction of negative acceleration is
opposite to the direction in which the body is moving.
Negative acceleration is also called deceleration or
retardation.
Gravitational Acceleration
Gravitational acceleration is the acceleration an object free falling in vacuum.
Regardless of the masses or compositions, all bodies accelerate at the same rate in a vacuum. This means that if there were no air friction, any two objects falling from the same height would always reach the earth surface simultaneously.
If a body is dropped from a certain height, it will start its motion towards earth. As it has a gravitational acceleration, its speed will keep on increasing till it reach the earth surface. If we neglect the air reistance, its velocity will be maximum when it will hit the ground.
The value of gravitational acceleration on earth is 9.8 m/s2 and is usually denoted by g.
If a body is falling downward, its speed will increase and gravitational acceleration is positive.
If a body is thrown upward, its speed will decrease and gravitational acceleration is negative. In this case body's velocity will decrease as it goes up and at certain height its velocity will become zero.