IMAGE FORMATION BY LENSES
In mirrors images are formed through reflection, but lenses form images through refraction. This is explained with the help of ray diagrams as follows:
Image formation in convex lens can be explained with the help of three principal rays shown in Fig.1
- The ray parallel to the principal axis passes through
the focal point after refraction by the lens.
- The ray passing through the optical centre passes
straight through the lens and do not change its direction
- The ray passing through the focal point becomes parallel to the principal axis after refraction by the lens.
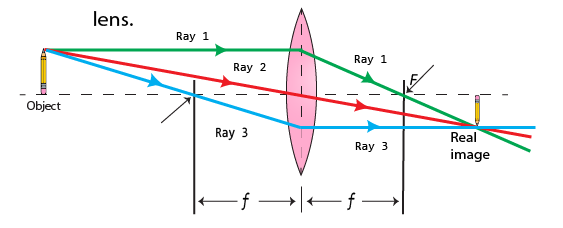
IMAGE FORMATION BY CONVEX LENS
Consider following cases:
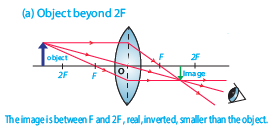
- When object is located at a distance greater than 2F, the image is between F and 2F, inverted, real and smaller than object.
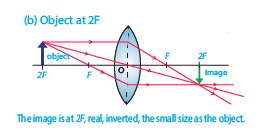
- When object is located at a distance 2F, the image is at 2F, inverted, real and same size of object.
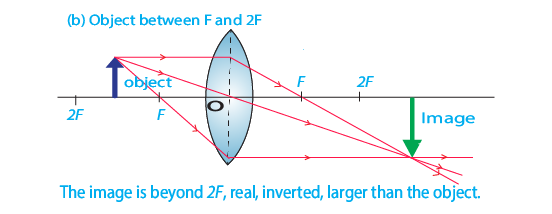
- When object is located between F and 2F, the image is beyond 2F, inverted, real and larger than object.
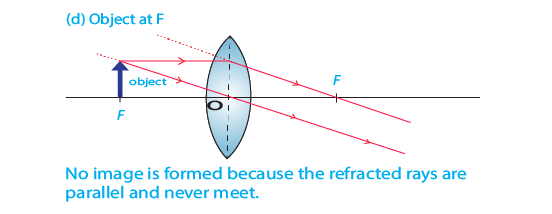
- When object is located at F, no image is formed as both rays become parallel to each other and never meet
- When object is located between F and lens, the image is behind object, virtual, erect and larger than object
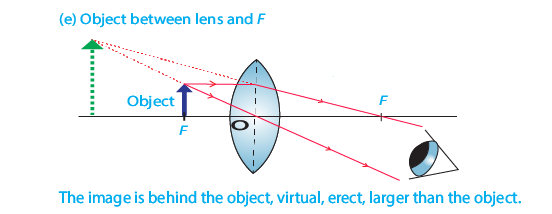
IMAGE LOCATION BY LENS EQUATION
Let an object OP is placed in front of a convex lens at a distance p. A ray PR parallel to the principal axis after refraction passes through focus F. Another ray PC meets the first ray at point P’ after passing through the optical centre C.
If this process is repeated for the other points of the object, a real and inverted image OP is formed at a distance q from the lens.
What is the size of image formed in a lens for particular distance of object from the lens? What is the nature of image, i.e., whether image is real or imaginary, erect or inverted?
Lens formula is a tool that we use to answer all such questions. We define lens formula as,
“The relation between the object and image distance from the lens in terms of the focal length of the lens is called lens formula”
$$ \frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{p} + \frac{1}{q}$$
Above Equation is valid for both concave and convex lenses. However, following sign conventions should be followed while using this equation to solve problems related to lenses.
Sign Conventions for Lenses:
Focal length:
- f is positive for a converging lens
- f is negative for a diverging lens.
Object Distance:
- p is positive, if the object is towards the left side of the
lens. It is called a real object.
- p is negative, if the object is on the right side of the
lens. It is called virtual object.
Image Distance:
- q is positive for a real image made on the right side of
the lens by real object.
- q is negative for a virtual image made on the left side
on the lens by real object.










