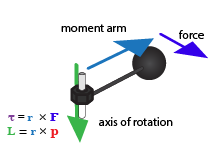
TORQUE OR MOMENT OF A FORCE
”The turning effect of a force is called torque or moment of the force”
RIGID BODY
A body is composed of large number of small particles. If the distances between all pairs of particles of the body do not change by applying a force then it is called a rigid body. In other words, a rigid body is the one that is not deformed by force or forces acting on it.
AXIS OF ROTATION
Consider a rigid body rotating about a line. The particles of the body move in circles with their centres all lying on this line. This line is called the axis of rotation of the body.
Examples:
Forces that produce turning effect are very common. Turning pencil in a sharpener, turning stopcock of a water tap, turning doorknob are some of the examples where a force produces turning effect.
Why the handle of a door is fixed near the outer edge of a door?
We can open or close a door more easily by applying a force at the outer edge of a door rather than near the hinge. Thus, the location where the force is applied to turn a body is very important.
Let us study the factors on which torque or moment of a force depends.
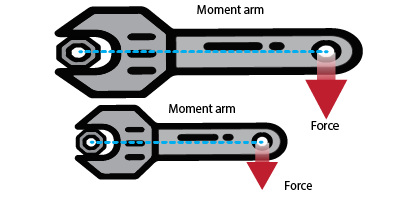 You might have seen that a mechanic uses a spanner as shown in figure.
To loosen or tighten a nut or a bolt. A spanner having long arm helps him to do it with greater ease than the one
having short arm. It is because the turning effect of the force is different in the two cases.
You might have seen that a mechanic uses a spanner as shown in figure.
To loosen or tighten a nut or a bolt. A spanner having long arm helps him to do it with greater ease than the one
having short arm. It is because the turning effect of the force is different in the two cases.
The moment produced by a force using a spanner of longer arm is greater than the torque produced by the same force but using a spanner of shorter arm.
LINE OF ACTION OF A FORCE
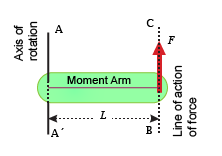
The line along which a force acts is called the line of action of the force. In figure line BC is the line of action of force F.
MOMENT ARM
The perpendicular distance between the axis of rotation and the line of action of the force is called the moment arm of the force. It is represented by the distance L in figure. The torque or moment of a force depends upon the force F and the moment arm L of the force. Greater is a force, greater is the moment of the force. Similarly, longer is the moment arm greater is the moment of the force. Thus the moment of the force or torque is determined by the product of force F and its moment arm L. Mathematically,
$$\tau = F \times L$$SI unit of torque is newton-metre (Nm). A torque of 1 N m is caused by a force of 1 N acting perpendicular to the moment arm 1 m long.
COUPLE:
A couple is formed by two unlike parallel forces of the same magnitude but not along the same line.
 When a driver turns a vehicle, he applies forces that produce a torque. This torque turns the steering wheel. These forces act on opposite sides of the steering wheel
and are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. These two forces
form a couple.
When a driver turns a vehicle, he applies forces that produce a torque. This torque turns the steering wheel. These forces act on opposite sides of the steering wheel
and are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. These two forces
form a couple.
A couple is formed by two unlike parallel forces of the same magnitude but not along the same line.
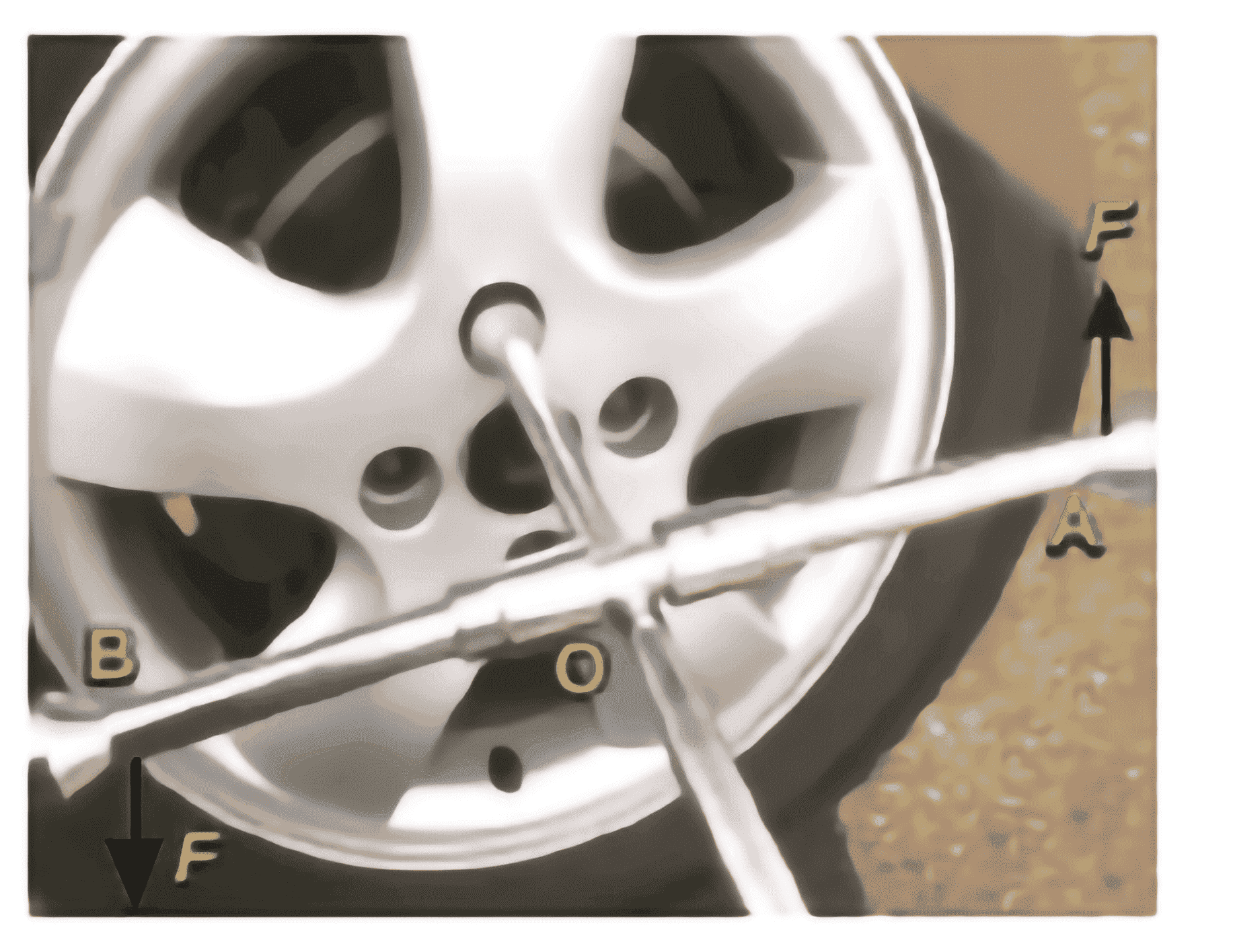
A double arm spanner is used to open a nut. Equal forces each of magnitude Fare applied on ends A and B of a spanner in opposite direction as shown in figure . These forces form a couple that turns the spanner about point O. The torques produced by both the forces of a couple have the same direction. Thus, the total torque produced by the couple will be $$Total \; torque \; of \; the \; couple = F \times OA + F \times OB $$ $$ = F (OA + OB)$$ $$Torque \; of \; the \; couple = F \times AB $$ Equation gives the torque produced by a couple of forces F and F separated by distance AB. The torque of a couple is given by the product of one of the two forces and the perpendicular distance between them.